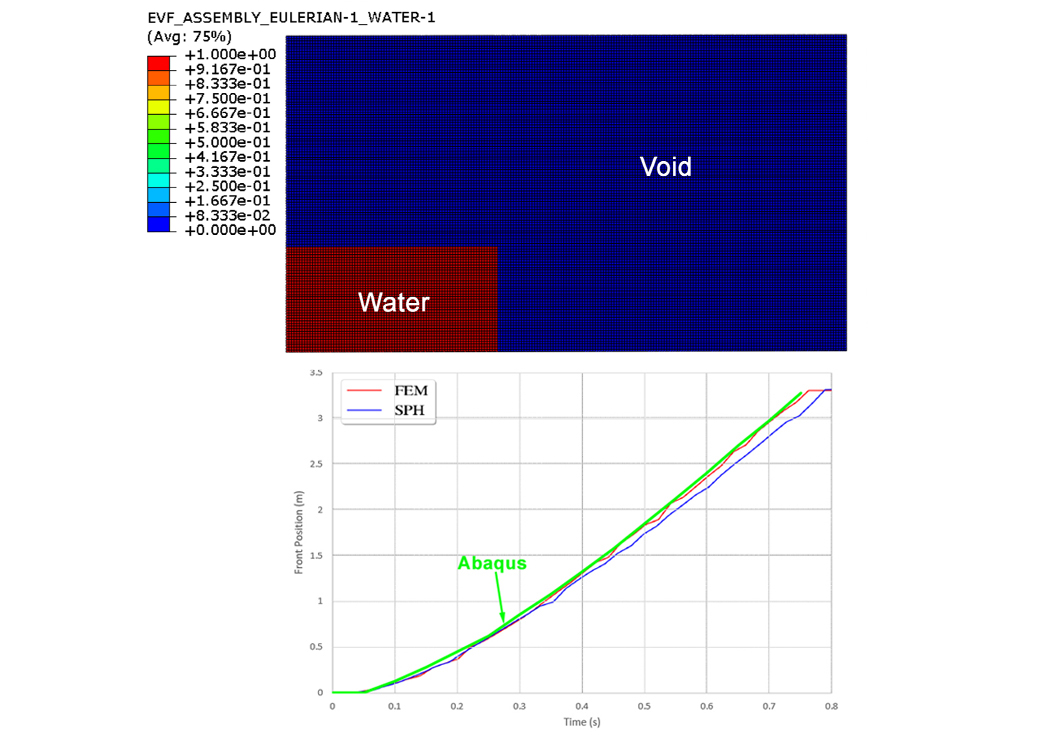
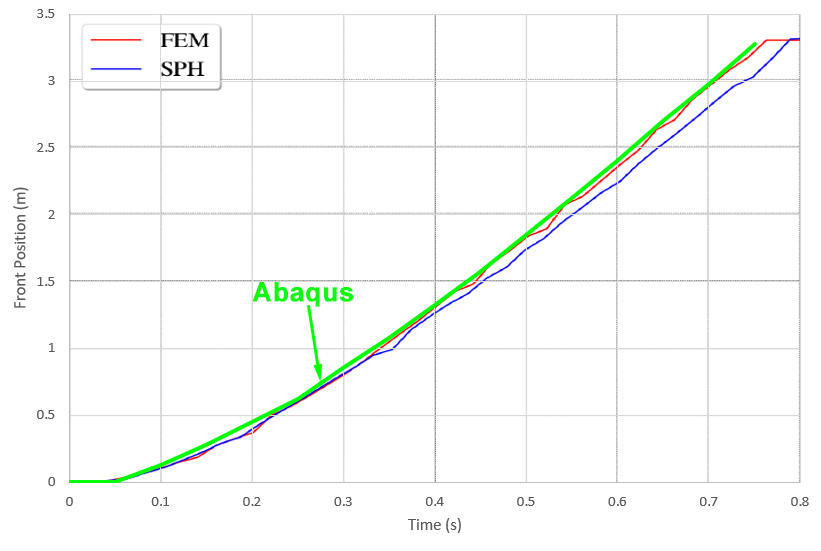
Fluid front position over time in the dam break problem in Abaqus
in this example we intend to calculate fluid front position over time in the dam break problem in the Abaqus software
In this example, the water column is subjected to the gravity load, causing the water column to collapse and the water to flow down on the ground
The Eulerian domain is a rectangle with the length and width of 5.3 by 3 meters. The Eulerian area is actually an area on which the water fluid can move in it. Here the water column has an elevation of 1 meter
Water properties include density of 1000 kg/m3 , viscosity of 0.001 Pa.s , speed of sound of 1500 m/s
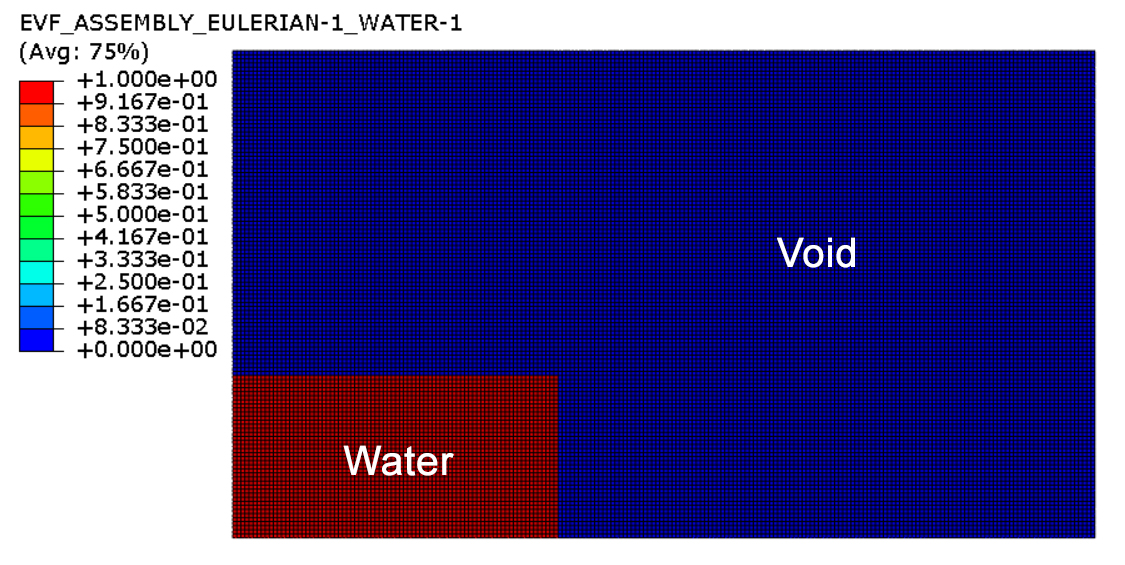
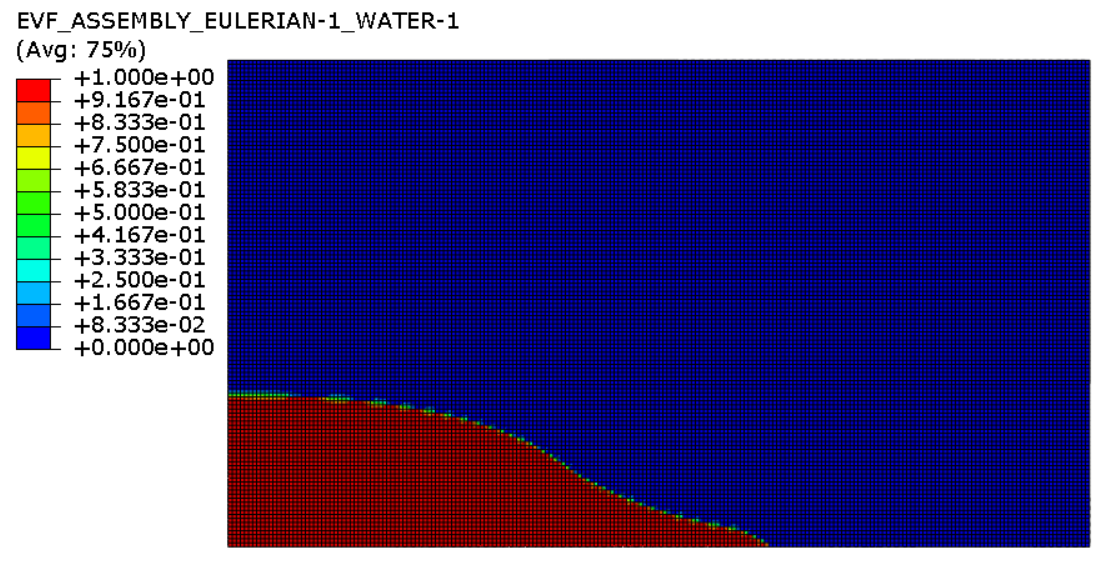
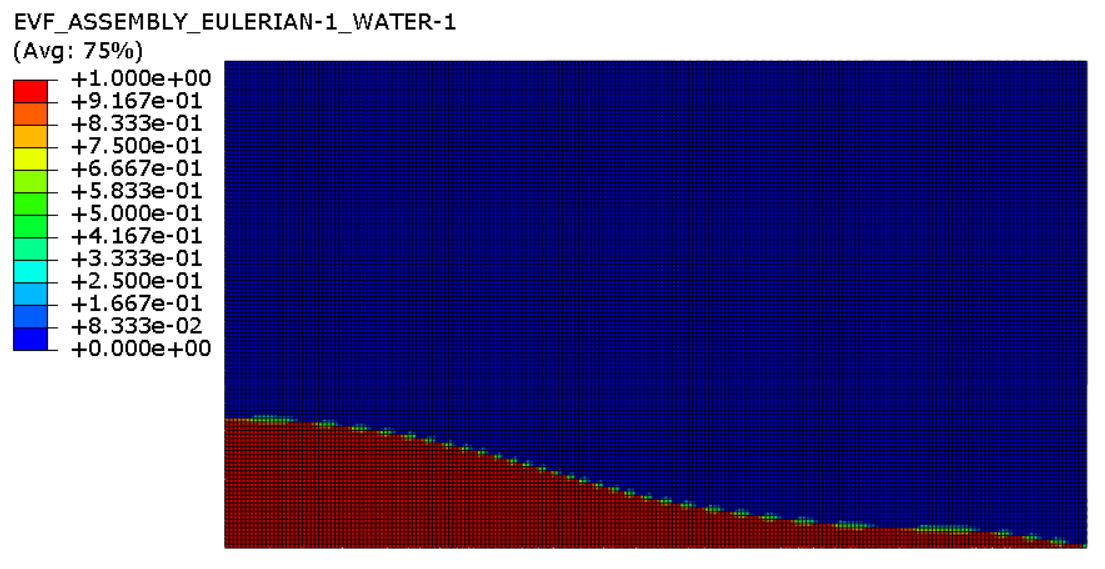
In this picture you can observe the Eulerian area as well as the initial place of the water fluid. The area of water has been marked out with red while the void area has been displayed by blue color in this picture
The Eulerian domain is a rectangle with the length and width of 10 by 5 meters. The Eulerian area is actually an area on which the water fluid can move in it. Here the water column has an elevation of 4.5 meters
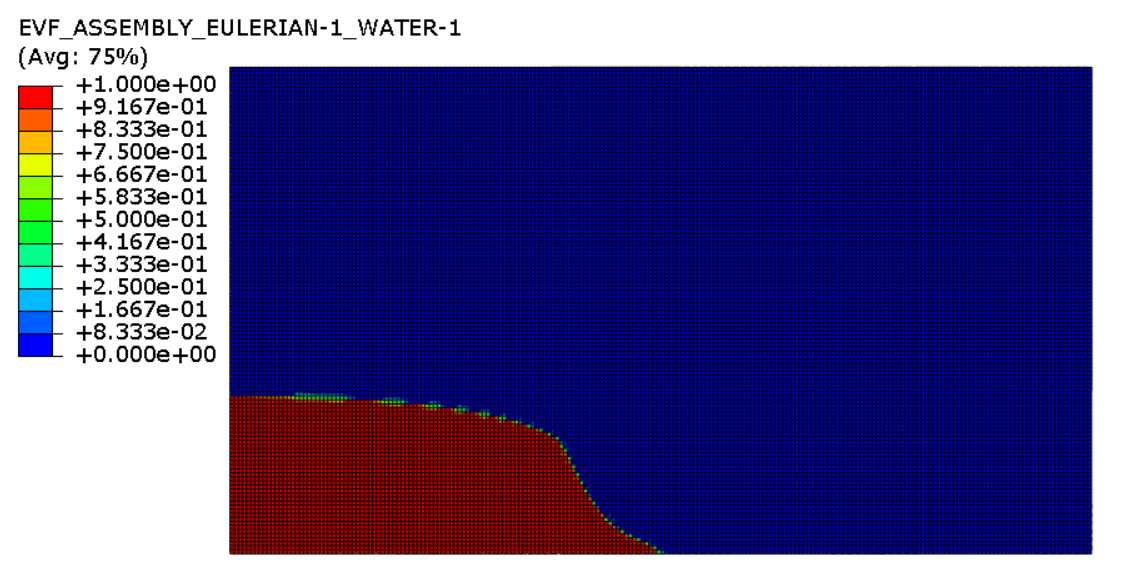
These pictures you can observe deformation of the water column in different time
This project has been validated, which means that the results obtained from Abaqus software are similar to the results of the article. In other words, this project is based on the article



There are no reviews yet.